Intestinal barrier : key to digestion and nutrient absorption
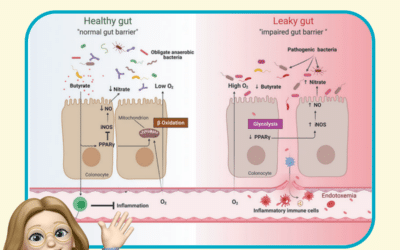
Unlock the mystery of your digestive system! In this edition, we explore the vital roles of digestion and nutrient absorption, essential for maintaining health. Digestion is the process by which foods are broken down into smaller molecules, or nutrients, making them...
gut-health : the key to general health
Have you ever wondered how your body turns the food you eat into the energy you need? The secret lies within the fascinating world of gut physiology. Your digestive tract is not just a simple tube for digestion—it’s a complex system designed to absorb essential...
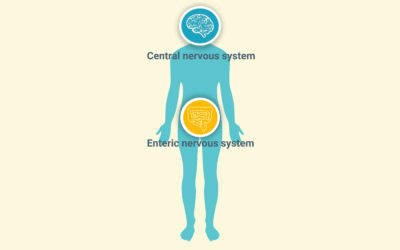
The gut-brain axis: exploring its role in health care
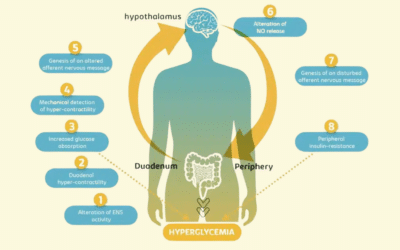
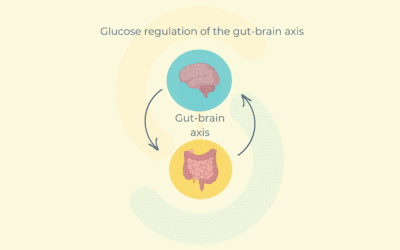
In the intestine, gut distension and nutrients are detected by mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, respectively. The activation of these receptors sends an afferent nervous message to the hypothalamus in the brain. In turn, the hypothalamus controls the glucose entry in tissues, and thus glycemia.
Type 2 Diabetes: the glucose regulation
In the intestine, gut distension and nutrients are detected by mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors, respectively. The activation of these receptors sends an afferent nervous message to the hypothalamus in the brain. In turn, the hypothalamus controls the glucose entry in tissues, and thus glycemia.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of maternal milk
The high hydrostatic pressure processing of donor milk may better protect preterm infants from gut and liver pathologies compared to Holder pasteurization, which is currently used in most human milk banks.
12-HETE enterosyne: new insights into glucose metabolism
The discovery of intestinal actors, such as enterosynes, able to modulate the ENS-induced duodenal contraction is an innovative approach. Among all the intestinal factors, the understanding of the role of gut microbes in controlling glycaemia remains a major target. For instance, we researched and demonstrated how the modulation of gut microbiota by prebiotics could permit the identification of novel enterosynes.
Glucose: a key player in gut motility and metabolic regulation
Targeting the enteric nervous system that controls gut motility is now considered as an innovative therapeutic way in T2D to limit intestinal glucose absorption and restore the gut‐brain axis to improve insulin sensitivity. So far, little is known about the role of glucose on duodenal contraction in fasted and fed states in normal and diabetic conditions.
How does the gut microbiota interact with our second brain?
Currently, the gut is considered a primary site for the development of pathologies that modify brain functions such as neurodegenerative (Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, etc.) and metabolic (type 2 diabetes, obesity, etc.) disorders. Deciphering the mode of interaction between microbiota and the brain is a real original option to prevent (and maybe treat in the future) the establishment of gut-brain disfunctions and associated pathologies.
Camu Camu extract: health benefits against metabolic disorders
The Amazonian forests are home to a shrub, the camu-camu, whose fruit could be of great help in the fight against obesity and metabolic diseases. This is described in our latest study published with the A-Mansia R&D team in the journal Metabolites.
Enteric nervous system : Galanin’s role in gut-brain axis
The enteric nervous system (ENS) plays a key role in controlling the gut-brain axis under normal and pathological conditions, such as type 2 diabetes. The discovery of intestinal actors, such as enterosynes, able to modulate the ENS-induced duodenal contraction is considered a pioneering approach.
Blood-brain barrier and beta-blockers: new insights into central effects
In addition to their classical mode of action in the brain, circulating factors may modulate the release of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) from endothelial cells that compose the blood-brain-barrier without entering the brain. Due to their high capacity to diffuse across membranes, ROS/RNS can reach neurons and modify their activity. This study investigates other mechanisms of actions in which beta-blockers may display a central effect without crossing the blood brain barrier.
White paper ENTEROSYS
« GUT IS THE LINK »
Our first white paper is now available !
Get inside the head of our co-founder Claude Knauf.
Come discover his background, his key dates, how he got the gut feeling and the link between enteric neurons and glycemic control as well as other health related areas.

Do you have a question about the contribution of gut models in your innovative research ?
Our team of experts will be delighted to answer all of your questions. We guide you in the design of an optimized protocol to meet your objectives and add value to your molecules with quick and concrete solutions.